Orbiter自带文档《Orbital Mechanics Primer》,轨道力学入门/导读,共三个部分:开普勒定律、万有引力定律和重力势能。
本文摘录第一部分:开普勒定律。基于Google翻译,手工修改了一些。请读者批评指正。
首先,要指出一点,开普勒和多普勒是两个人。开普勒定律是天体运动的规律,而多普勒效应是波动的一个现象。
百度百科:开普勒定律
百度百科:多普勒效应
Kepler's laws of planetary motion
开普勒行星运动定律
From the study of observational data collected by astronomer Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler was able to infer his famous three laws of planetary motion, which can be stated as follows:
通过研究天文学家第谷·布拉赫收集的观测数据,约翰内斯·开普勒推断出他著名的行星运动三大定律,内容如下。
Kepler's first law
开普勒第一定律
Each planet moves in an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
每个行星都在一个以太阳为焦点的椭圆轨道上运行。
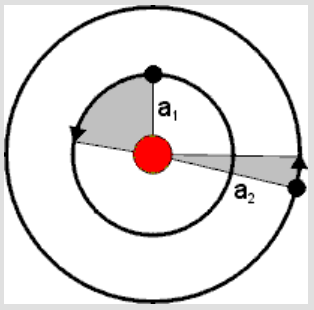
Kepler's second law
开普勒第二定律
The line between the Sun and a planet sweeps over equal areas in equal time.
太阳和行星之间的连线在相同的时间内扫过的面积相同。
Kepler's third law
开普勒第三定律
开普勒第一定律
The cube of the semimajor axis of a planet's orbit is proportional to the square of its period of revolution.
行星轨道半长轴的立方正比于其公转周期的平方。
Kepler's laws are purely phenomenological: They provide a concise description of the observed data, but don't attempt to explain the physical causes of the motion.
开普勒定律纯粹是现象学(就是根据这些数据,提出了对这一现象的几个描述)的:三大定律简明扼要地解释了观测到的数据,但并未试图解释天体运动的物理原因。
Such a physical explanation was achieved by Sir Isaac Newton, who formulated the three fundamental dynamic laws of motion and the law of gravitation, from which Kepler's laws can be derived.
艾萨克·牛顿爵士(Sir Isaac Newton)则给出了物理原理的解释。牛顿导出了三大运动定律和万有引力定律,利用他所提出的这些定律则可以推导出开普勒定律。
Using Newtonian dynamics, it also follows that Kepler's laws are only approximations of the true motions. Strictly they apply only to two-body problems, while in a multi-body system such as the solar system, the influence of other celestial bodies causes perturbations in the orbits. However, in most cases these perturbations are small, so that Kepler's laws provide a good model of reality.
利用牛顿动力学,可以知道开普勒定律只是真实运动的近似。严格地说,开普勒定律仅适用于两体问题(双星问题),而在诸如太阳系的多体系统中,其他天体的影响会导致轨道的摄动(扰动)。然而,在大多数情况下,这些扰动都很小。因此,开普勒定律为现实世界的仿真提供了一个良好的近似。
The derivation from Newton's laws also shows that orbital trajectories are not limited to ellipses, but may also have a parabolic or hyperbolic shape. In general, the orbits in a 2-body problem are described by conic sections. Ellipses describe periodic orbits, while parabolic and hyperbolic orbits are non-periodic.
牛顿定律的推论同样也表明天体的运动轨迹除了椭圆,也可能会是抛物线或双曲线。通常,双星(双体)问题的轨道可以由圆锥曲线描述。椭圆可以描述周期性轨道,而抛物线和双曲线则描述非周期轨道。